Introduction

User experience(UX) has become increasingly important in recent years as the competition among businesses has grown. In order to keep up with change and disrupt the respective markets, many organizations have placed a great emphasis on creating amazing customer experiences. The key to standing out among competitors and providing a superior customer experience is through User-Centered Design.
User-Centered Design, also known as UCD or Human-centered design, is “a process used in the development of user interfaces or applications that puts the user first and foremost during the entirety of the project” according to Wikipedia. This process is not only beneficial for the users but also helps businesses save time and money. In this guide, we will take a look at the UCD process and how it can be used in order to create amazing digital products.
By following this guide, you will be able to create an effective UX design process that meets your specific needs. Let’s get started!
1. What is user-centered design (UCD)?

User-centered design (UCD) is a process used in the design of products, services, and digital experiences that focuses on the needs and expectations of the end user. The ultimate goal of UCD is to create products that are both easy to use and appealing to the people who will be using them. To achieve this, designers must take into account the user’s needs when making decisions about the layout, functionality, and overall look of the product. Every element of the design must be evaluated from the perspective of the user, in order to ensure that it meets their needs. This process can be time-consuming and require a lot of feedback from users, but the end result is usually a product that is both highly usable and visually appealing.
2. Tips for getting started with UCD
If you’re interested in getting started with UCD, here are some tips to help you get started:
- Do your research – The first step in any UCD project is to gain a deep understanding of your users. Who are they? What are their needs? What motivates them? The better you understand your users, the better equipped you’ll be to design solutions that meet their needs.
- Take a user-centered approach – When it comes to design, always keep the user in mind. Every decision should be made with the user in mind. This includes everything from the overall layout of the site to the specific wording of buttons and labels.
- Test – A major part of UCD is testing early and often. This allows you to constantly refine your designs based on feedback from real users. Testing can be done through paper prototypes, usability studies, or even A/B testing on live sites or apps.
Following these tips will help you get started with UCD and create designs that are truly user-centered.
3. Steps of the UCD process; from Discover to Deliver
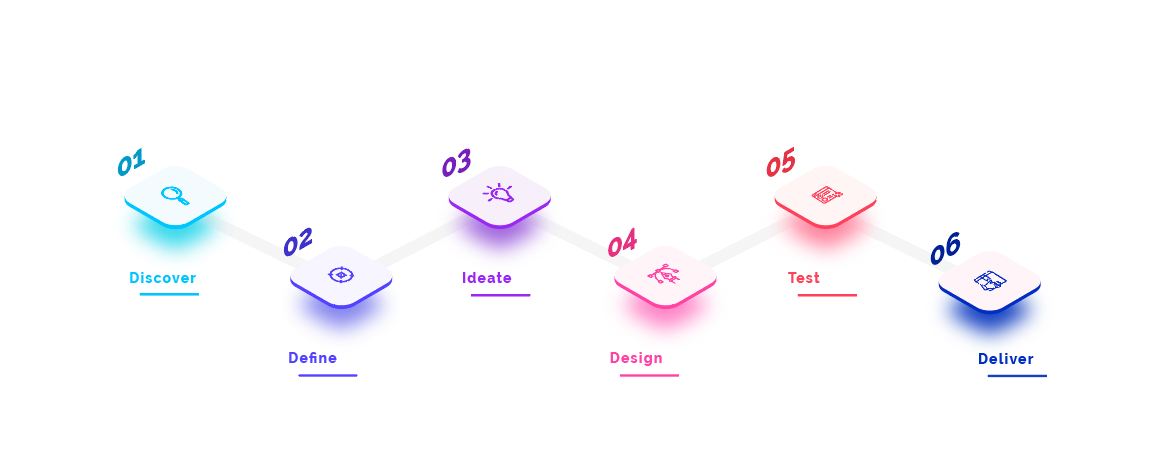
Discover
The first step in the User-Centered Design process is Discover. During this phase, designers work to understand the problem and the users. This is done through the following methods.
- Competitive Analysis
In this phase, UX designers take a close look at the competition to see how the competitors are solving similar problems. This helps to understand the market and the users better.
- Audience Definition
After Competitive Analysis, UX designers move on to Audience Definition. During this phase, designers define who the target audience is and look at demographics, interests, and needs of the target audience.
- Content Survey
In this phase, UX designers take an inventory of the content that already exists. This helps to understand what content is necessary and how it can be organized.
- User Research
During this phase, UX designers conduct interviews and surveys with users to understand their needs. This helps to validate the assumptions made in the previous steps and make sure the product or service is meeting user needs.
- Market Research
After User Research, designers move on to Market Research. In this phase, designer analyze the market to understand what is already out there and what might be possible for the project. This helps to understand the competition and make sure the product or service is unique.
- Design Strategy
In this phase, UX designers create a plan for how the product or service will be designed. This includes creating a style guide, Wireframes, and prototypes.
- UX & Analytics Audit
In the UX & Analytics Audit, the designers take a close look at the product or service to see how it is performing. This helps to improve the UX of the product.
Define
The second step in the User-Centered Design process is Define. During this phase, ux designers work to establish the goals and objectives for the project. This is done by creating personas, user flows, and mapping.
- Affinity Mapping
In this phase, UX designers group ideas together to find relationships. This helps to understand the problem better and come up with solutions.
- User Persona
After Affinity Mapping, UX designers move on to User Persona. During this phase, designers create a persona of the user. This helps to understand the user better and design for their needs.
- Storyboard
In this phase, UX designers create a storyboard of the user experience. This helps to visualize the flow of the product or service and understand how users will interact with it.
- Empathy Mapping
In Empathy mapping, UX designers map out the user’s journey. This helps to understand the user’s needs and design for their experience.
- User Journey Mapping
After Empathy Mapping, UX designers move on to User Journey Mapping. In this phase, they create a map of the user experience. This helps to visualize the flow of the product or service and understand how users will interact with it.
Ideate
In the Ideate phase, UX designers create a plan for how the product or service will be designed. This includes creating user flow, card sorting, and Information architecture.
- User Flow
Here, designers map out the user’s journey. This helps to understand the user’s needs and design for their experience.
- Card Sorting
In this phase, designers sort cards into groups. This helps to understand the relationships between ideas and come up with solutions.
- Information Architecture
In the Information Architecture phase, UX designers organize information. This helps to understand the structure of the product and design for it.
Design
After the Ideate phase, ux designers move on to the Design phase. In this phase, they work to create a visual design for the product or service. This includes creating a style guide and prototypes.
- Low Fidelity Wireframes
During this phase, UX designers create rough sketches of the product. This helps to understand the layout and design of the product.
- Wireframes
In this phase, UX designers create a skeletal outline of a design that is used to communicate the basic structure and content of a page or app.
- Interactive Prototypes
An interactive prototype is a digital or physical representation of a design that allows people to test out its functionality and give feedback.
- Guides & Design Systems
Here designers create guides and design systems. This helps to document the work and keep track of the designs.
- Visual Design (UI)
In Visual design, designers work to create a visually appealing design for the product or service. This includes creating color schemes, typography, and iconography.
- Interaction Design
In this phase, designers design the interactions between the user and the product. This includes the buttons, menus, and other elements that the user interacts with.
Test
After the product or service is designed, UX designers move on to Test. In this phase, designers work with users to test the product or service. This helps to understand how users interact with the product or service and what they think of it.
- User Testing/Usability Test
In this phase, designers test the product with users. This helps to understand how well the product works and what needs to be improved.
- Test Report
After the Test phase, UX designers move on to the Test Report. This will help to review the findings and make necessary changes to improve the design.
- Review
In this phase, designers work with stakeholders to review the results of the test and make decisions about how to proceed with the project.
- Approval
Here, designers get approval from stakeholders. This helps to ensure that the product is ready to develop.
Deliver
The final step in the User-Centered Design process is Deliver.
In this phase, ux designers work to deliver the project to the client. This includes creating a final report and delivering the project files.
- UX Documentation
After the project is delivered, UX designers create UX documentation. This includes a final report, design guidelines, and user flows.
- Launch Support
After the project is launched, UX designers provide support to ensure that the product or service is successful. This includes providing feedback and troubleshooting issues.
- Maintenance Support
Once the product or service is up and running, UX designers provide maintenance support. This includes providing updates and new features as needed.
4. Benefits of using the UCD process in product development
A UCD process is a structured approach to product development that can help to ensure that products are designed with the user in mind.
There are many benefits to using the UCD process in product development. Perhaps the most important is that it can help to create products that are actually used and enjoyed by the intended users. Products developed without taking into account the needs and want of users are often difficult or impossible to use, leading to frustration and ultimately abandonment.
In addition, the UCD process can help to save time and money in the development process. By focusing on the user experience from the start, designers can avoid having to make major changes later on in the development process when it becomes apparent that the product is not usable.
Finally, using a UCD process can help create a product that is more likely to be successful in the marketplace. People are more likely to purchase and recommend products that they find easy and enjoyable to use.
If you are planning to develop a new product, consider using a user-centered design process to help ensure that your product is usable, enjoyable, and successful.
Conclusion
UCD is essential for any product to create amazing customer experiences and stay ahead of competitors. By putting users first and constantly gathering data, businesses are able to evolve the products and services at a relatively high speed. Implementing UCD does require buy-in from upper management as well as dedicating resources towards research analysis; however, the long-term benefits greatly outweigh the costs. Use this guide to get started on your journey toward long-lasting success. If you’re interested in product design and development, 5nart can help. We specialize in helping companies get started with user-centered design, and we would be happy to answer any questions you have or provide more information about our services. Thanks for reading!



